Understanding GI and Its Significance for Community-Based Economies
A Geographical Indication (GI) is a sign or name used to identify products whose quality, reputation, or distinct characteristics stem from a specific geographical origin. Well-known Thai examples include Nonthaburi Durian (often called “Durian Non”), Hom Mali Rice from Thung Kula Rong-Hai, Doi Tung Coffee, and Lamphun Silk, among others.
In Thailand, registering GI holds considerable importance:
- It protects local heritage by preventing unauthorized use of a product’s geographically linked name.
- It adds marketing value and can increase income for local producers, fostering rural economic development in a sustainable manner.
- It promotes quality standards and cultural preservation, since producers must maintain consistent product specifications.
According to the latest data from the Department of Intellectual Property (DIP), specifically the Geographical Indications Division, as of January 30, 2025 (B.E. 2568), Thailand has approved 247 registered GI products. This includes:
- 224 Thai products, covering all 77 provinces, broken down into:
- 152 from the agricultural sector
- 39 from the handicraft sector
- 33 from the industrial sector
- 23 foreign GI products recognized in Thailand, originating from 9 countries
These figures illustrate the rapid growth and widespread recognition of GI products across the country. Every Thai province now boasts at least one product that meets the DIP’s criteria for GI registration, highlighting immense potential for further expansion.

Key Criteria for GI Registration in Thailand
Producers or community groups aiming to register a GI must provide comprehensive documentation. The DIP’s Geographical Indications Division outlines five core criteria:
- Unique Quality or Characteristics: Demonstrate how your product differs from similar goods produced elsewhere, whether in aroma, taste, color, texture, or other physical and chemical properties.
- Link Between the Product and its Origin: Explain how geographical factors—such as climate, soil, local ingredients, or traditional know-how—influence the product’s distinct qualities.
- History and Reputation: Provide evidence of long-standing recognition or consumer trust. This can span from local fame to national or international acclaim.
- Quality Standards and Control Measures: Clearly define production standards, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing processes, as well as inspection protocols to ensure consistent quality.
- Defined Production Area and Local Raw Materials: Specify the geographical boundary where the product is produced, confirming that key inputs and production processes originate from that location.
Government Agencies Involved in GI Registration

Department of Intellectual Property (Ministry of Commerce)
The Department of Intellectual Property (DIP) is Thailand’s primary authority for GI registration, working through its Geographical Indications Division. Applicants must prepare their submissions according to DIP guidelines, and can consult with DIP officers for assistance on technical requirements.

Provincial Commerce Offices
These offices help facilitate local GI applications. Producers or communities can submit an initial GI request or seek advice from the Provincial Commerce Office, which will liaise with the DIP on documentation and follow-up.

Other Supporting Agencies
- Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives (e.g., Department of Agricultural Extension), providing training to farmers on improving production quality for GI compliance.
- Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT), promoting GI products through cultural and agro-tourism initiatives.
- Biodiversity-Based Economy Development Office (Public Organization), supporting the sustainable use of local biological resources.
Additionally, policy-level leaders such as the Deputy Prime Minister and the Minister of Commerce have been prioritizing the expansion of GI listings across all provinces, aiming to open new marketing channels domestically and internationally.
Examples of Notable GI Products in Thailand
Thailand offers a wide range of GI items, including agricultural produce, processed foods, and artisanal crafts, spanning every region:
Northern Region
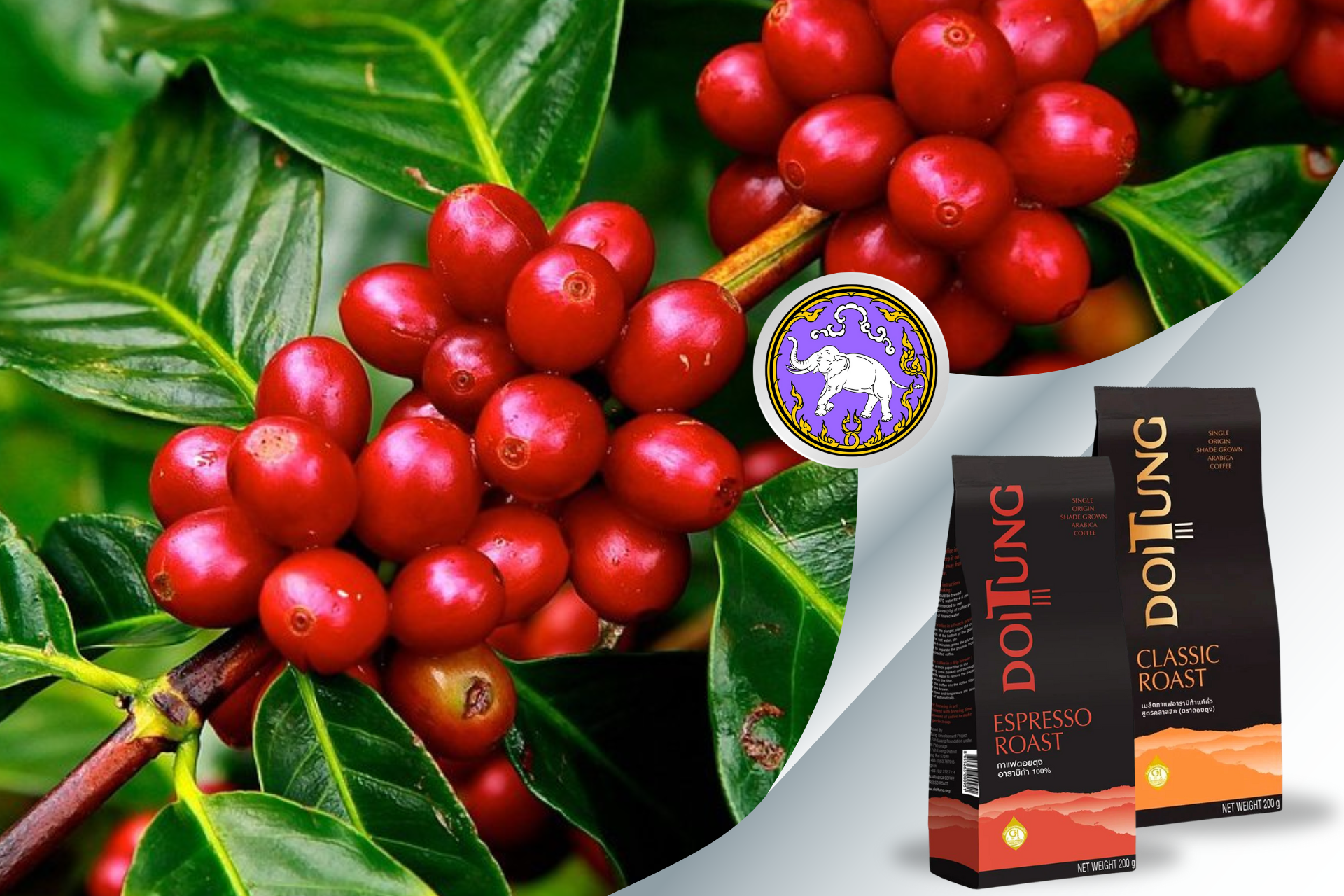
- Doi Tung & Doi Chang Coffee (Chiang Rai): globally renowned.
- Phulae Pineapple (Chiang Rai): prized for its sweet, juicy flavor.
- Lamphun Silk (Lamphun): known for intricate weaving techniques.
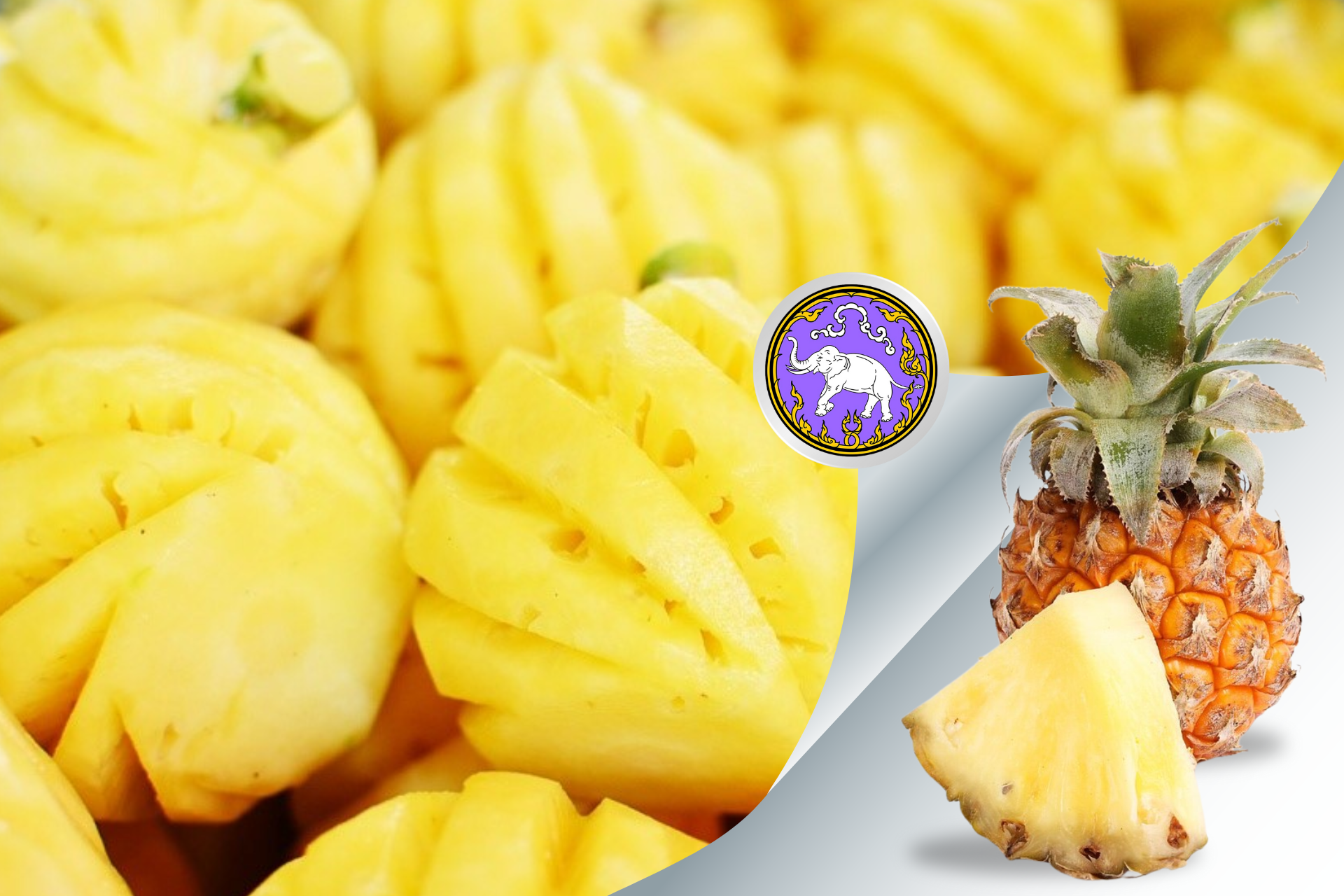



Northeastern Region (Isan)
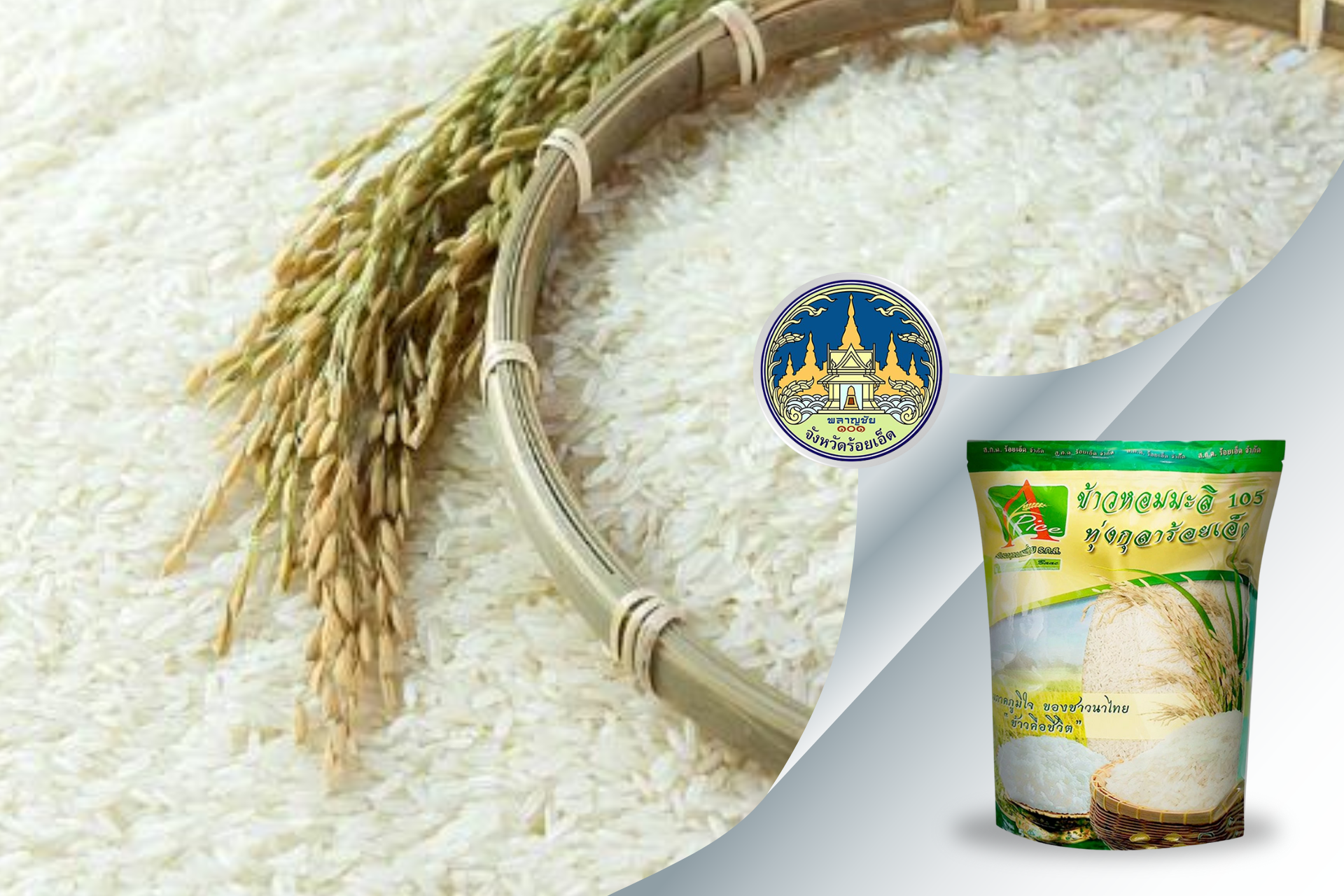
- Hom Mali Rice from Thung Kula Rong-Hai (Roi Et, Yasothon, Surin, Maha Sarakham, Si Sa Ket): revered for its fragrant, soft grains.
- Ban Chiang Pottery (Udon Thani): cultural heritage site with ancient ceramic arts.
- Praewa Silk (Kalasin): famous for its delicate, intricate patterns.
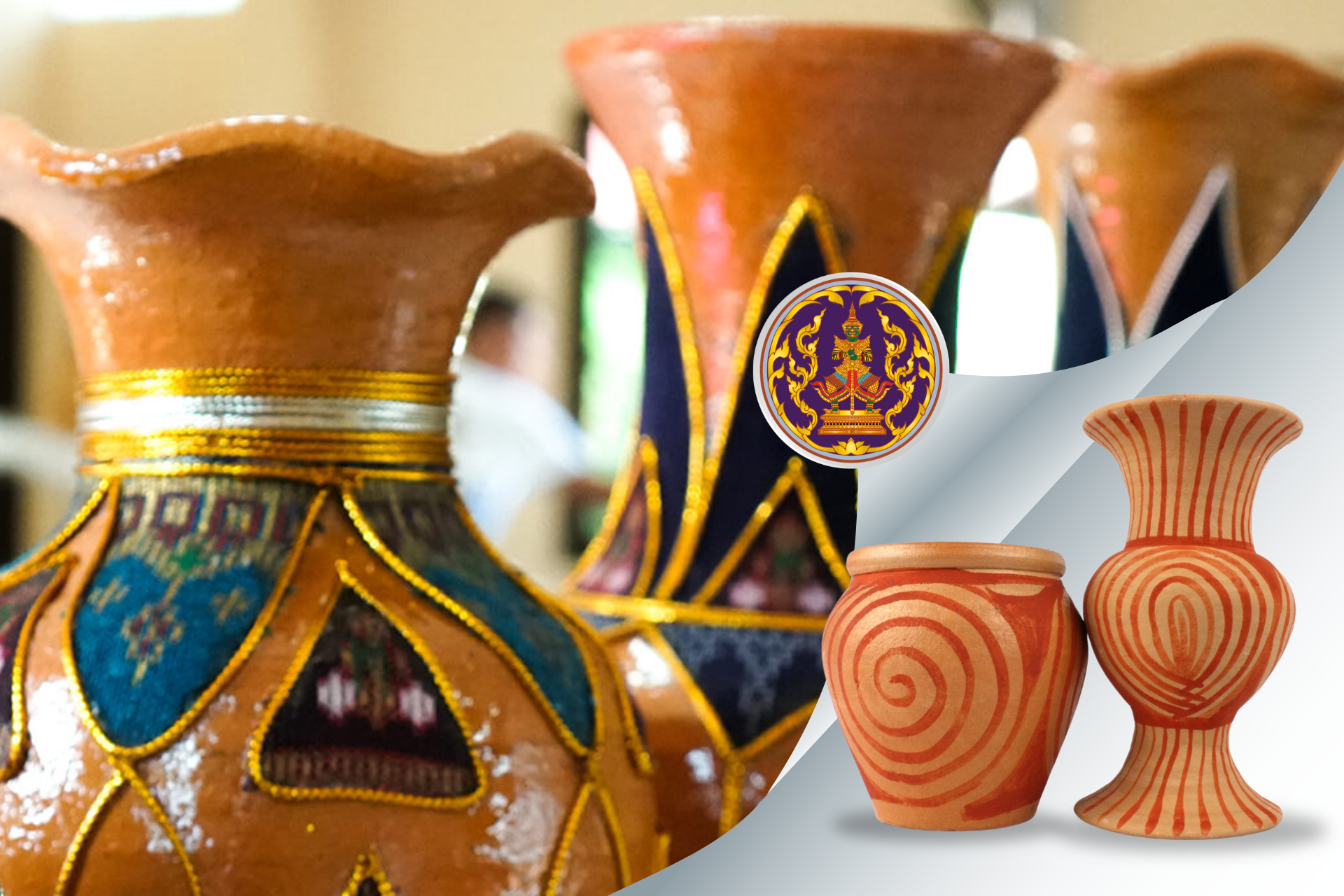



Central Region
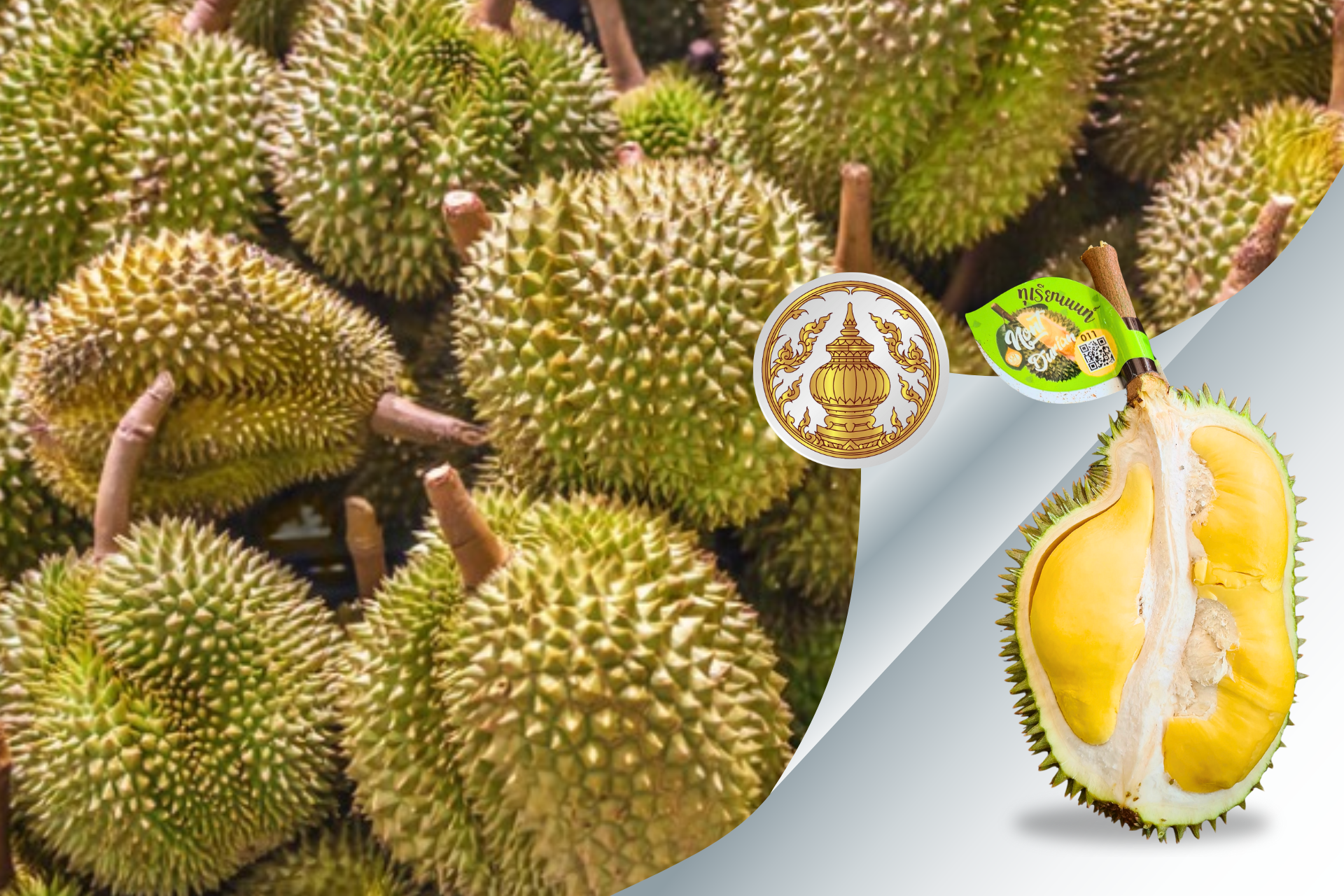
- Nonthaburi Durian (Nonthaburi): celebrated for its rich, unique taste.
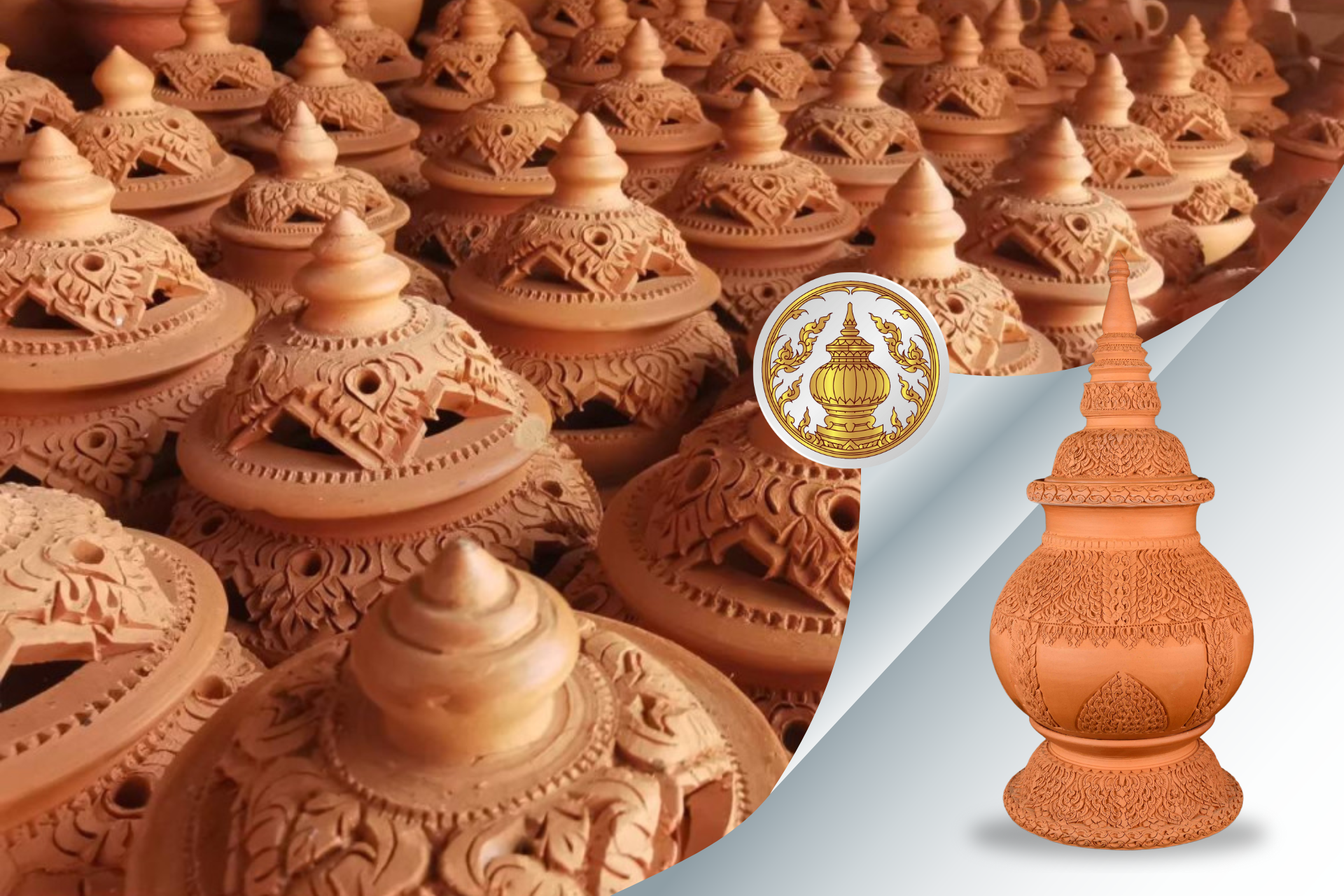
- Koh Kret Pottery (Nonthaburi): handcrafted heritage of local artisans.
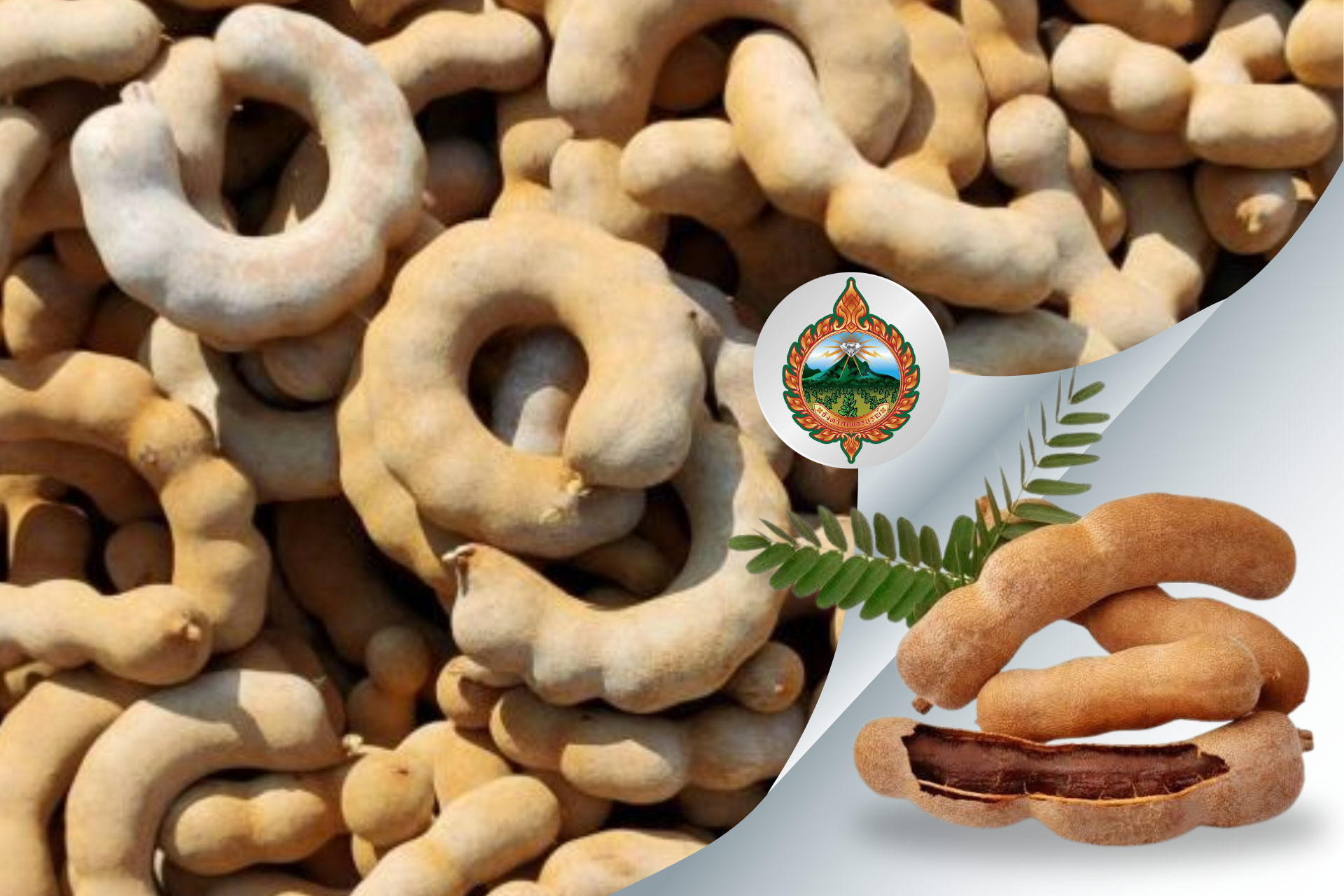
- Phetchabun Sweet Tamarind (Phetchabun): characteristically sweet with a mild aroma.



Southern Region
- Pink Flesh Pomelo (Pak Phanang District, Nakhon Si Thammarat): distinguished by its red-tinted pulp and balanced sweet-tart flavor.
- Sangyod Rice of Phatthalung (Phatthalung): nutritious and high in antioxidants.
- Chaiya Salted Eggs (Surat Thani): well-known for a just-right balance of salty richness.
- Trang-Style Roasted Pork (Trang): noted for its special marinade and roasting technique.
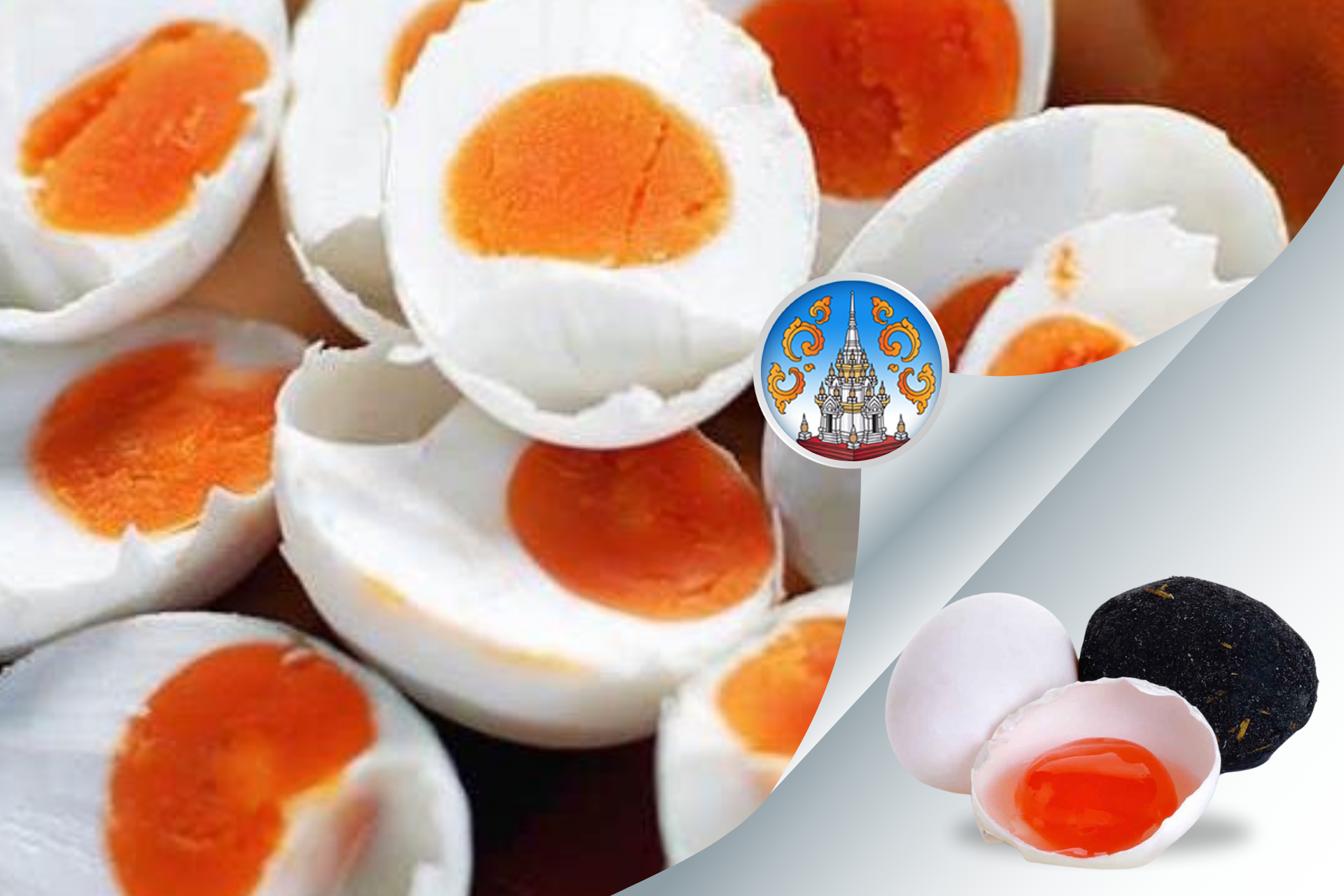



Such region-specific identities resonate with consumers both domestically and internationally. After obtaining GI registration, many products see increased market visibility and premium pricing.
Benefits of GI for Producers, Consumers, and Community Development
1. Protecting Product Names and Enhancing Negotiating Power
GI registration under Thailand’s Geographical Indications Protection Act B.E. 2546 (2003) prevents unapproved usage or counterfeiting of a product’s name, thus preserving its hard-earned reputation.
2. Raising Market Value and Community Income
GI status draws consumer interest and boosts prices, leading to significant income growth for producers. DIP estimates that GI products in Thailand may collectively surpass 71 billion baht (approx. USD 2+ billion) in annual market value with effective marketing.
3. Driving Continuous Quality Control
GI producers must maintain consistent standards per their registered specifications. This ongoing quality assurance fosters sustainable product development and preserves local craftsmanship for future generations.
4. Promoting Experiential Tourism
Many GI products align with tourism experiences. Visitors may tour coffee plantations in Doi Tung or durian orchards in Nonthaburi, boosting rural hospitality and creating additional income streams.
5. Offering High-Standard Products to Consumers
The “GI mark” indicates authenticity and standardized production methods, giving consumers confidence in quality and origin.
6. Preserving Cultural Heritage and Local Wisdom
GI mechanisms encourage communities to keep traditional skills and cultural practices alive, strengthening local identities and ensuring socio-economic resilience.
Challenges and Obstacles in GI Development
-
Lack of Awareness and Understanding:
Some communities are unaware of the benefits or procedures for GI registration, lacking group organization or systematic evidence collection.
-
Maintaining Ongoing Standards:
Post-GI recognition, stakeholders must continuously monitor product quality. Limited resources or personnel can hinder compliance in certain groups.
-
Marketing and Packaging Skills:
Even with quality products, a strong brand image, modern packaging design, and diversified distribution channels are crucial for market success. Many local producers need external guidance in these areas.
-
Law Enforcement and Anti-Infringement Measures
Despite legal protections, detecting and prosecuting counterfeit GI products remains challenging, requiring vigilance by government bodies and consumer awareness.
-
Price and Accessibility
GI goods often command higher prices, and distribution channels can be limited. Some consumers may find the products too expensive or difficult to source.
-
International GI Registration
For producers aiming to export, applying for GI protection abroad is a separate, complex process involving foreign legal frameworks and significant time and costs.
Key Legal Framework: Geographical Indications Protection Act B.E. 2546 (2003)
Enforced since 2004, this Act aligns with WTO TRIPS requirements. It defines “Geographical Indication” and outlines:
- Registration procedures
- Penalties for infringement
- Provisions for revocation
The Department of Intellectual Property oversees GI applications, approvals, or cancellations in Thailand. Although Thailand has not yet joined the Lisbon Agreement (Geneva Act) on Appellations of Origin and Geographical Indications, its domestic law provides comprehensive GI protection consistent with international norms.
TIBD’s Role in Supporting GI Registration
As an organization committed to innovation and business development, TIBD offers a range of consulting services and strategic support for businesses and community groups interested in GI registration. Our expertise includes:
- GI Fundamentals: Explaining benefits, registration steps, and key requirements to prepare communities or enterprises.
- Documentation and Planning: Compiling technical research, historical records, and detailed specifications for DIP submission.
- Product Quality Enhancement: Advising on process improvements, innovation adoption, and packaging design to meet demanding market standards.
- Market Strategy for GI Products: Assisting producers in promoting GI goods domestically and internationally. We provide insights on branding, storytelling, and marketing communications.
- Network and Partnership Development: Linking producers with key partners, such as government institutions, private companies, and international organizations. TIBD acts as an integrator, fostering collaboration for mutual benefit.
Drawing on our strengths in innovation and business development, TIBD is poised to serve as a “professional consultant” propelling Thai and foreign-owned GI products to international markets. GI-labeled goods are increasingly sought after worldwide, and TIBD can help maximize their competitive potential.
GI: A Catalyst for Sustainable Local Growth
A Geographical Indication (GI) is more than just a name denoting origin. It is both a marketing and legal tool, safeguarding local products and driving economic value while ensuring that the unique cultural identity of Thai communities endures.
However, registering GI can be complex—from technical documentation and quality standards to global marketing. TIBD plays a pivotal role in guiding producers through these challenges. By leveraging our consultancy and connections, Thai producers and foreign stakeholders alike can overcome bottlenecks and seize new business opportunities that GI status can unlock.
Once a product attains GI recognition, consumers exhibit heightened trust and a willingness to pay premium prices, fueling local economic growth and sustaining cultural heritage for generations to come.
If you or your organization is interested in GI registration in Thailand or seeking opportunities to develop and innovate your products, TIBD stands ready to assist. We look forward to supporting Thai and international partners in achieving long-term success through robust GI strategies. Click