Black cumin
Nigella sativa L., often known as Black cumin, is a member of the Ranunculaceae family. The seeds have a rough exterior surface, are entirely black, rigid, and have a faint odour. Indian origin It is present in the majority of Middle Eastern and southern European nations. Black candle seeds are utilised in the Trirattakula coordinate formula in ancient Thai medicinal remedies. To nourish the fire element, expel intestinal gas, or according to traditional knowledge in the National Drug Board statement. Hom Thepchit, Hom Nawakot, Clove Medicine, Elemental Confluence Pills, and Prasaplai all include black candle seeds. It can help with wind, dizziness, vomiting, colic, indigestion, treating stomach discomfort, and relieving menstruation pain.
Black Cumin Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of black seed contains volatile oils such as fatty acids Linoleic acid, Oleic acid, Palmitic acid, volatile oils such as Thymoquinone, Thymol, Limonene, p-cymene, 4-terpineol, Terpene, Terpenoid, alkaloids such as Nigellidine, Nigellimine, Sterol, saponins such as Alpha-hederin, Kaempferol, Quer (Antiviral). It is also used to treat abscesses (Abscess), skin inflammation (Eczema), blood pressure (Anti-hypertensive), Asthma (Anti-asthmatic), Diabetic activity (Diabetic activity), Vascular (Cardiovascular activity), and to help protect the liver (Hepatoprotective action) and deworming (Anti-parasitic).
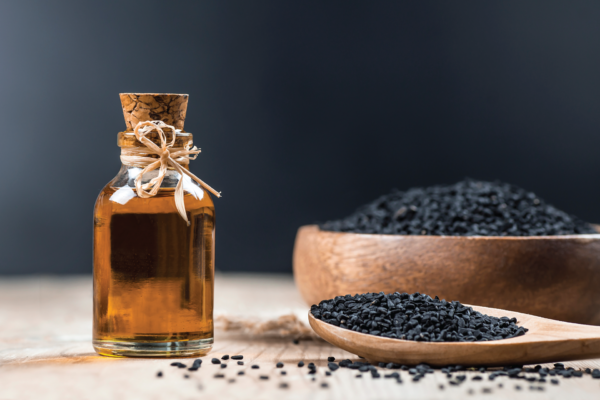


The use of Black Cumin in the Cosmetic Industrial
In addition to fighting free radicals, black candle can inhibit cytokines such as IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10, which are precursors to inflammation (Anti-inflammatory), aid in wound healing (Would Healing), inhibit acne-causing bacteria (Acne Vulgaris), and promote collagen formation beneath the skin layer to form a skin barrier (Skin barrier).
The use of black candle in the Supplement Industrial
Black cumin is used as an option for the relief or prevention of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and depression, as well as to reduce anxiety, nourish the brain, liver, digestive system, heart, and blood vessels, and to learn about antioxidants (Anti-oxidation) and anti-inflammatory (Anti-inflammatory) compounds that boost the body’s immune system (Immunomodulatory). According to study, it has the capacity to help stop cancer cells (Anti-cancer) such as breast cancer, colon cancer, and bladder cancer, prevent diabetes (Anti-obesity), and decrease fat in the blood (Anti-dyslipidemic). Helps postmenopausal women maintain hormonal balance. Increases the density of bone cells (Bone Regenerative) against platelet adhesion.
Properties of Black Cumin
Anti-inflammatory
pain relief anti-inflammatory

Skin barrier
Strengthen the skin’s protective barrier. from bacteria and dirt

Immunity
strengthen the immune system for the body

Anti-Alzheimer’s
Improve memory, nourish the brain, prevent Alzheimer’s
The advancement of Black Cumin research
Black cumin can be further improved in a variety of methods, including the creation of raw material sources, extraction processes, emulsions, and encapsulation development processes to improve the stability of the extract and delivery to the target organ. In the development of research and natural extracts, TIBD now collaborates with major research institutes both locally and abroad, such as Japan and Brazil. However, if you are interested in co-investing in the form of research development, commercial patent development, or continuing to make product formulae under your brand, you may contact the firm through any channel.
Reference
Hannan, Md, et al. “Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.): A Comprehensive Review on Phytochemistry, Health Benefits, Molecular Pharmacology, and Safety.” Nutrients 13.6 (2021): 1784.
Mariod, Abdalbasit Adam, et al. “Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of phenolic rich fractions obtained from black cumin (Nigella sativa) seedcake.” Food Chemistry 116.1 (2009): 306-312.
Datta, Animesh K., et al. “Black cumin (Nigella sativa L.)–a review.” Journal of plant development sciences 4.1 (2012): 1-43.
Oskouei, Zahra, Maryam Akaberi, and Hossein Hosseinzadeh. “A glance at black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent, thymoquinone, in ischemia: a review.” Iranian journal of basic medical sciences 21.12 (2018): 1200.