Tamarind Extract
Tamarind (Tamarind), scientific name Tamarindus indica L., is an African plant of the Fabaceae family. The species is then found throughout Asia and Latin America. Tamarind has been used in Thai herbal recipes since King Ramkhamhaeng’s reign, and it is the provincial tree of Phetchabun. Tamarind leaves have the ability to heal cough, dysentery, and drive blood. The meat in the sheath possesses phlegm-biting and constipation-curing qualities. Tamarind bark contains contraceptive effects, heals, seeds, properties, drives parasites, nourishes joints, treats diarrhoea, and bark properties to treat swollen gums and chronic wounds.
Chemical Composition of Tamarind Extract
Tartaric acid, Acetic acid, Malic acid, Succinic acid, Amino acid, Pyrazine, Thiazole, and fatty acids such as Palmitic acid, Oleic acid, Linoleic acid, and Eicosanoic acid were discovered in various regions of the tamarind. Tamarind leaf includes Lupanone, Lupeol, and Linonene, while Tamarind bark has Apigenin, Catechin, Procyanidin B2, Taxifolin, Eriodictyol, and Naringenin, and Tamarind seed contains Amyrin, Compesterol, Sitosterol, and Procyanidins Procyanidin B2 epicatechin, among other things. Tamarind extract was discovered to be effective in inhibiting microorganisms (Antimicrobial) and Antioxidant activity (Anti-oxidation) that is superior to Butylated hydroxyl anisole. And it also contains ascorbic acid, anti-inflammatory (Anti-inflammatory) has an anti-diabetic effect (Antidiabetic activity) has the effect of protecting the liver from toxins (Hepatoprotective) contributes to the heart and blood vessels (Cardiovascular system).
Applications of Tamarind Extract in Cosmetic Industries
According to research, tamarind extract has antibacterial activity (Anti-bacterial) against Burkholderia pseudomallei, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella paratyphi, Bacillus subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus, as well as antifungal activity (Anti-fungal) against Aspergillus Niger and Candida albicans. Tamarind bark and leaf extracts have wound healing, anti-inflammatory effects (Anti-inflammatory activity) by inhibiting the Because of the Flavonoid, Anthocyanidin, and Proanthocyanin makeup.


Applications of Tamarind Extract in Supplement Industries
Because to the high amount of Malic acid, Tartaric acid, and Potassium acid, tamarind extract has moderate laxative qualities (Laxative characteristics). It exhibits anti-diabetic effect in moderate and severe rats (Mild and severe diabetic) and those with high blood sugar levels (Hyperglycemia). It can help prevent artery hardening (Antiatherosclerosis) caused by fat buildup, boost the immune system Immunomodulatory by limiting leukocyte migration and lymphocyte multiplication, and accelerate the process of phagocytosis.
Properties of Tamarind extract
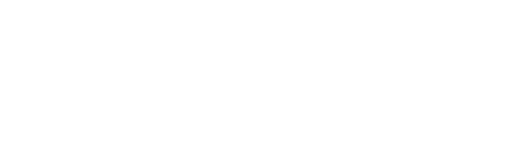
Wound healing
Has the effect of helping to heal wounds
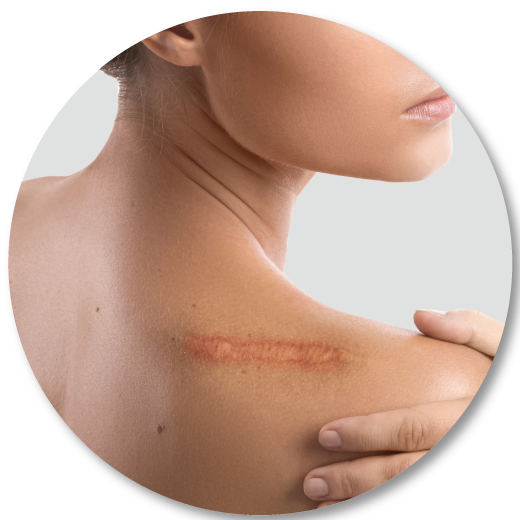
Anti-inflammatory
Pain relief anti-inflammatory
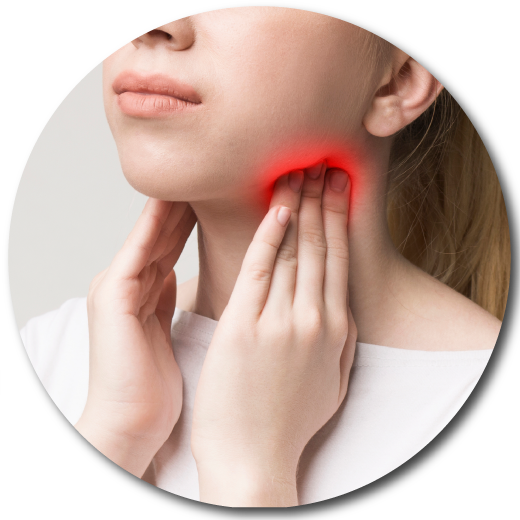
Anti-diabetes
Lowering blood sugar levels for diabetics

Immunity
Strengthen the immune system for the body
Further development of research on tamarind extract
At the moment, tamarind extract forms and tamarind products are being developed to improve the stability of extracts or the extraction process of raw material sources. The tamarind portion utilised in the extraction and development of products that are stable and enhance the effectiveness of the active components. In the development of research and natural extracts, TIBD now collaborates with major research institutes both locally and abroad, such as Japan and Brazil. However, if you are interested in co-investing in the form of research development, commercial patent development, or continuing to make product formulae under your brand, you may contact the firm through any channel.
Reference
Bhadoriya, S. S., Ganeshpurkar, A., Narwaria, J., Rai, G., & Jain, A. P. (2011). Tamarindus indica: Extent of explored potential. Pharmacognosy reviews, 5(9), 73.
Ahmad, A., Ahmad, W., Zeenat, F., & Sajid, M. (2018). Therapeutic, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Tamarindus indica: A review. International Journal of Unani and Integrative Medicine, 2, 14-19.
Kuru, P. (2014). Tamarindus indica and its health related effects. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 4(9), 676-681.
Zohrameena, S., Mujahid, M., Bagga, P., Khalid, M., Noorul, H., Nesar, A., & Saba, P. (2017). Medicinal uses & pharmacological activity of Tamarindus indica. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 121-133.